Understanding the Renault Cyber Attack and Its Impact
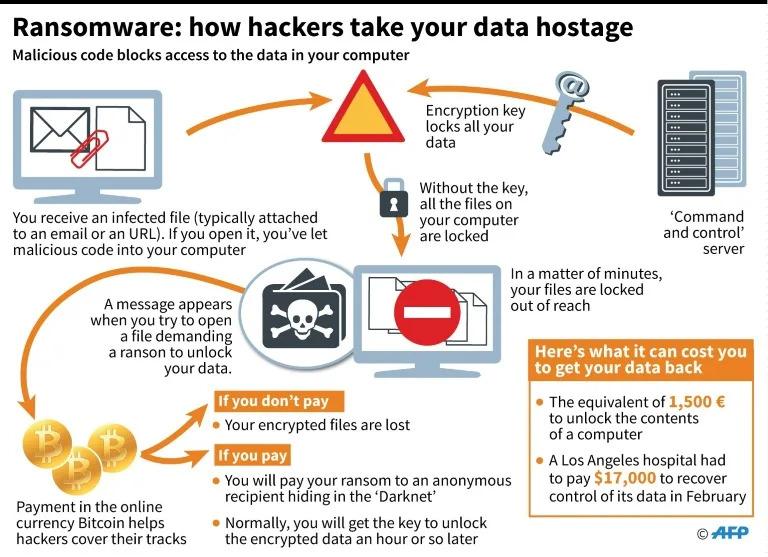
Introduction
The cyber attack that targeted Renault, a leading French automobile manufacturer, underscores the rising threat of cybercrime in the automotive sector. As digital technology becomes increasingly integrated into vehicle systems, the vulnerability of these systems to cyber threats poses significant risks to manufacturers and consumers alike.
The Cyber Attack Overview
In recent weeks, Renault confirmed that it had been the victim of a substantial cyber attack, prompting the company to initiate emergency protocols to contain the breach. The attack reportedly occurred through a sophisticated phishing campaign that compromised employee email accounts, leading to unauthorized access to sensitive operational data.
Extent of the Breach
Initial reports indicate that the cyber attack may have disrupted production lines and hampered the company’s ability to fulfil orders effectively. While Renault has stated that customer data remains secure, the breach has raised alarm bells regarding the potential for further exploitation of vulnerabilities within its supply chain. Industry experts suggest that the attack could have far-reaching implications, particularly in light of the growing trend of cyber attacks targeting critical infrastructure sectors, including automotive.
Company’s Response
In response to the attack, Renault has collaborated with cybersecurity experts to analyse the breach and strengthen its digital infrastructure. The company is not only focusing on remediation but also embarking on a comprehensive review of its cybersecurity policies and training for employees to prevent future incidents. Renault’s proactive approach is part of a broader trend among automotive manufacturers to invest heavily in cybersecurity as the industry evolves.
The Bigger Picture
The Renault cyber attack is part of a worrying trend observed across various industries where cyber criminals are leveraging advanced tactics to exploit vulnerabilities. According to a recent report from cybersecurity firm Cybersecurity Ventures, cybercrime is projected to cost the global economy over $10.5 trillion annually by 2025. This reinforces the need for robust cybersecurity measures across all sectors, including automotive.
Conclusion
The recent Renault cyber attack serves as a stark reminder of the increasing prevalence of cyber threats in our interconnected world. As manufacturers continue to integrate technology into their products and processes, the necessity of investing in cybersecurity becomes paramount. Consumers and stakeholders alike must remain vigilant regarding data security while pushing manufacturers to adopt stronger protective measures. The aftermath of this event will likely shape how automotive companies approach cybersecurity, necessitating an industry-wide shift towards more resilient digital frameworks.
