Understanding Inflation: Current Trends and Implications
The Importance of Inflation in Today’s Economy
Inflation has become a central topic of discussion in economic circles and among the general public in recent months, especially as real-world experiences with rising prices have increasingly affected everyday life. As economies continue to recover from the challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic, inflation is at the forefront of concerns for consumers, businesses, and policymakers alike.
What is Inflation?
Inflation is defined as the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services rises, eroding purchasing power. This economic phenomenon is typically expressed as a percentage increase. A moderate level of inflation is considered normal, but high inflation can lead to decreasing consumer confidence and purchasing power.
Current Trends in Inflation
Recent data from the Office for National Statistics reveals that the Consumer Prices Index (CPI) inflation rate in the UK soared to 6.7% in September 2023, significantly up from previous months. This sharp increase has been attributed to several factors, including supply chain disruptions, the ongoing energy crisis, and increased demand as economies continue to reopen. Additionally, the cost of living crisis has prompted widespread calls for government action to offset the impact on consumers.
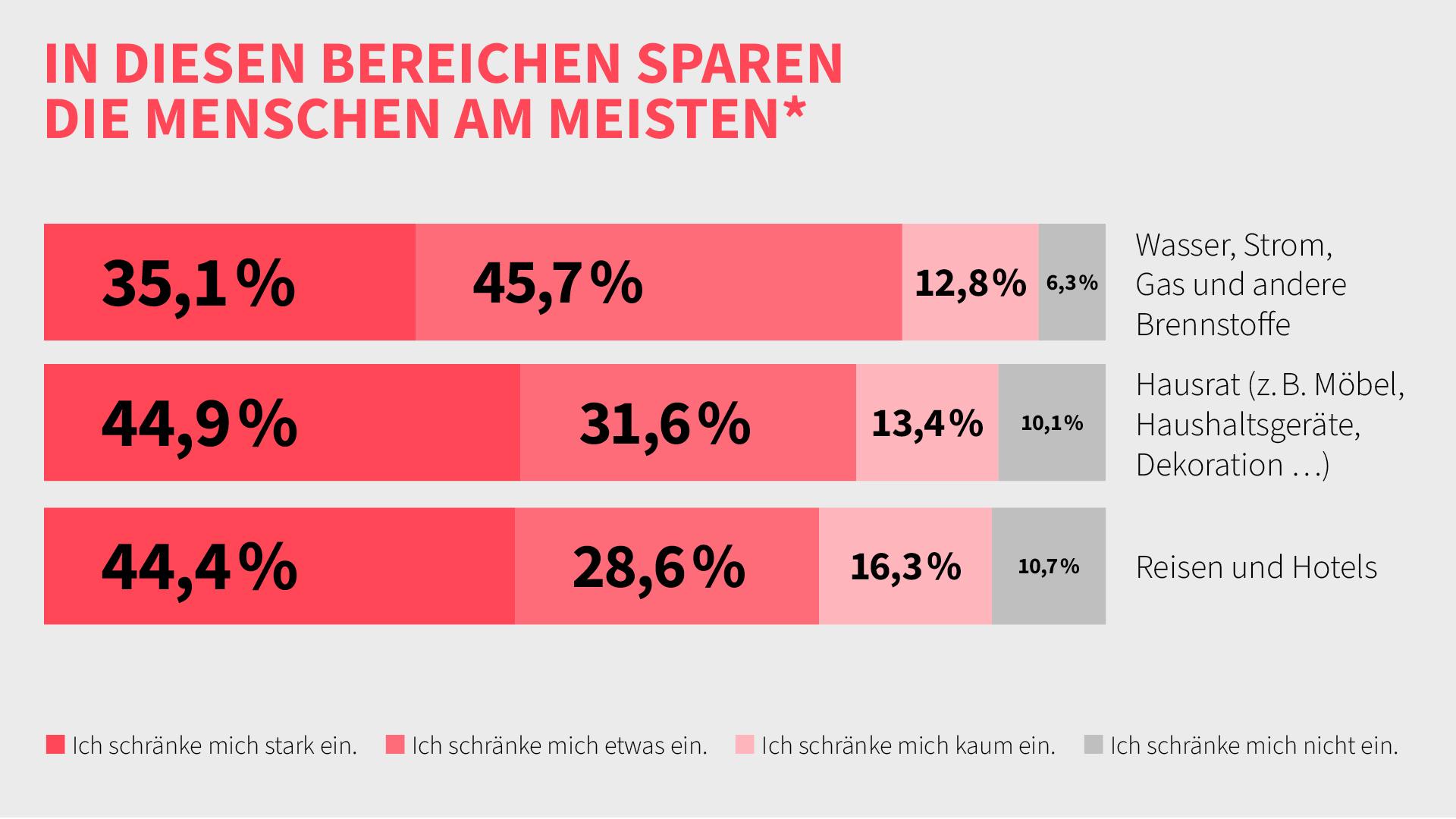
Impact of Inflation on Consumers
Consumers are feeling the brunt of rising prices, particularly in sectors such as food, energy, and transport. The Bank of England has acknowledged the difficulty many households are experiencing as their income cannot keep pace with inflation. With rising costs, many are forced to make tough decisions on budgets, spending less on either discretionary items or essential goods.
Economic Consequences
For businesses, inflation presents challenges to both operational costs and consumer demand. Companies are faced with increasing prices for raw materials and labour, which may, in turn, lead to higher prices for consumers, creating an inflationary cycle. Furthermore, the central bank’s approach to managing inflation through interest rate adjustments could impact borrowing costs, further influencing investment and spending behaviours in the economy.
Conclusion: The Path Forward
As inflation continues to rise, its implications for both consumers and businesses are paramount. Policymakers will need to navigate a delicate balance between stimulating economic growth and controlling inflation. With ongoing uncertainties such as geopolitical tensions and climate-related issues, monitoring inflationary trends will be essential for future economic planning. Consumers, meanwhile, may need to adapt to changing economic conditions, making informed financial decisions in an unpredictable environment. As the situation evolves, staying informed will be crucial for navigating the complexities of inflation.
