Understanding UK Inflation: Current Trends and Impacts
Introduction
Inflation in the United Kingdom has emerged as a critical issue affecting the economy and everyday life. As the cost of living continues to rise, understanding the factors driving inflation and its implications is essential for both policymakers and consumers. In recent months, UK inflation rates have hit levels not seen in decades, sparking discussions about potential government interventions and economic strategies.
Current Inflation Rates
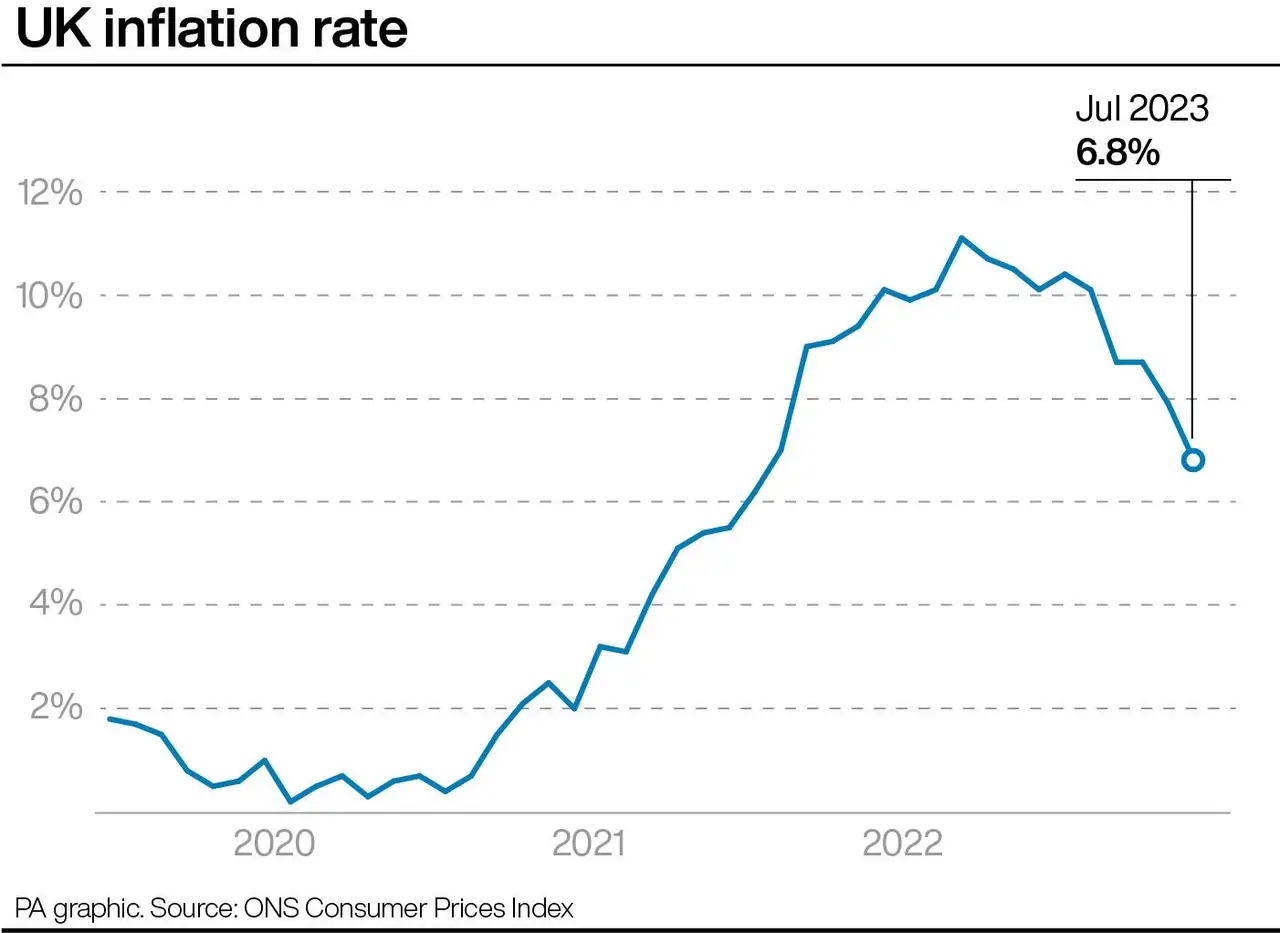
As of October 2023, the annual inflation rate in the UK stands at 6.7%, significantly above the Bank of England’s target of 2%. This increase can be attributed to several factors including higher energy prices, supply chain disruptions, and increasing food costs. The most recent data from the Office for National Statistics (ONS) highlights sharp rises in the cost of utilities and essential goods, which have a disproportionate effect on low-income households.
Impact on Consumers
Rising inflation directly impacts consumer spending power. The price of groceries, fuel, and housing has surged, forcing many families to make tough financial decisions. For instance, research shows that the average household is spending approximately £200 more per month compared to the previous year, leading to increased borrowing and reduced savings. Additionally, that inflationary pressure is forcing many consumers to reassess their budgets and spending habits.
Government Response
In response to these challenging inflation figures, the UK government has been exploring various monetary and fiscal policies. The Bank of England has raised interest rates twice in the past six months in an effort to curb inflation, although this carries the risk of slowing down economic growth. Furthermore, proposals for tax relief and subsidies on energy bills are under consideration to alleviate pressure on households.
Economic Outlook
Looking ahead, economists are divided on how inflation will trend in the coming months. Some experts anticipate that inflation may begin to ease as energy prices stabilise and supply chains recover. However, others warn of persistent inflationary pressures if wage growth does not keep pace with rising costs. The uncertainty surrounding global economic conditions and unforeseen events may also have a significant impact on inflation rates.
Conclusion
UK inflation remains a vital topic due to its wide-reaching effects on the economy and society. As consumers adapt to new financial realities, the government and Bank of England’s responses will play a crucial role in shaping future economic stability. Understanding these dynamics can help readers navigate the challenges posed by inflation and make informed decisions in an evolving economic landscape.
