Exploring the Significance of Gen Z Years
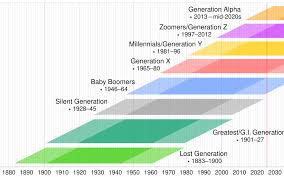
Introduction to Gen Z
Generation Z, often referred to as Gen Z, comprises individuals born approximately between 1997 and 2012. Understanding the characteristics and behaviours of this generation is crucial not only for marketers and business leaders but also for educators, parents, and policymakers. As the first generation to grow up with smartphones and social media as integral parts of their lives, Gen Z’s experiences, challenges, and aspirations are reshaping societal norms and economic landscapes.
Defining Traits of Gen Z
Gen Z is recognised for their advocacy around social issues such as climate change, racial equality, and mental health awareness. According to a recent report from McKinsey, 75% of Gen Z members believe it is essential for brands to take a stance on social and political issues. Their values are often reflected in their consumer behaviour; they prefer purchasing from brands that prioritise sustainability and ethical practices.
The Digital Natives
This generation has been labelled ‘digital natives’ as they have grown up in an era dominated by technology. With 94% owning a smartphone, Gen Z is incredibly connected, utilising various social media platforms for communication, education, and entertainment. The Pew Research Center indicates that TikTok, Instagram, and YouTube are the most popular platforms among Gen Z, influencing trends and cultural exchanges worldwide.
Economic Impact
As Gen Z enters the workforce, their preferences are likely to disrupt traditional workplace norms. A survey by Deloitte reveals that 50% of Gen Z individuals are interested in working remotely, emphasising their desire for flexibility and work-life balance. This may lead companies to adapt their corporate structures to attract and retain young talent. Furthermore, as consumers, Gen Z is set to spend over $140 billion annually, which will profoundly influence marketing strategies and product offerings.
Challenges Faced by Gen Z
Despite their characteristics, Gen Z faces numerous challenges, primarily related to mental health. Reports indicate that anxiety and depression rates are significantly higher among Gen Z compared to previous generations. This has led to increased awareness and advocacy for mental health resources, driving societal conversations and changes in school systems and workplaces.
Conclusion: A Future Shaped by Gen Z
As Generation Z continues to mature and assert themselves in various sectors, their impact will be felt for years to come. Their emphasis on social responsibility, technological integration, and mental wellness will likely shape the values of subsequent generations. For businesses, understanding Gen Z’s expectations and behaviours will be critical in fostering meaningful engagement. As they become the leaders and decision-makers of the future, the significance of the Gen Z years will undoubtedly influence societal dynamics and global trends.
