The Rising Concern of Ultra Processed Foods
Introduction
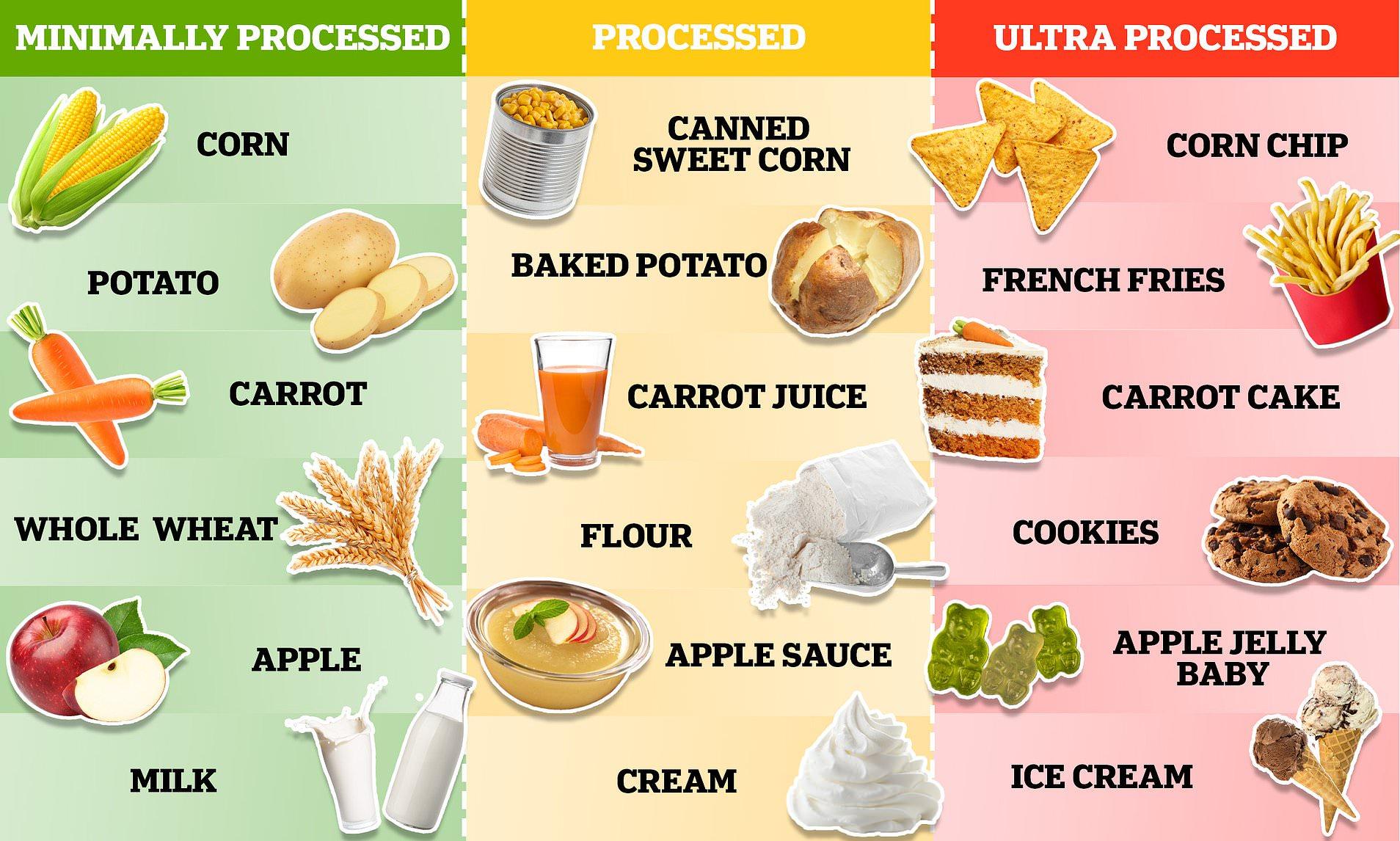
Ultra processed foods (UPFs) have become a significant part of modern diets, marked by their high levels of additives and low nutritional value. As more people rely on convenience and ready-to-eat options, understanding the implications of consuming these products is increasingly important. With research linking UPFs to various health issues, it’s essential for consumers to be informed about what they are eating and how it impacts their wellbeing.
The Nature of Ultra Processed Foods
Ultra processed foods are defined as industrial formulations made mostly or entirely from substances derived from foods, such as oils, fats, sugars, starches, and proteins. They often include artificial flavours, preservatives, and emulsifiers. Common examples include sugary drinks, packaged snacks, instant noodles, and reconstituted meat products.
Health Implications
Recent studies have highlighted numerous health concerns associated with UPFs. Research published in the BMJ Open indicates that diets high in ultra processed foods are correlated with an increased risk of obesity, heart disease, and even certain cancers. A 2021 report from the World Health Organization (WHO) outlined the potential for UPFs to contribute to unhealthy weight gain and metabolic syndromes, alarming researchers and public health officials alike.
The Global Trend
The global market for ultra processed foods is rapidly expanding. According to a report from the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), the consumption of UPFs has increased dramatically in both developed and developing countries. This trend raises concerns about dietary patterns and nutritional standards across the globe. Countries such as the UK and the USA have seen significant shifts in agricultural and food production policies that favour the processing industry.
Raising Awareness and Solutions
In light of these health risks, experts are calling for greater awareness and education regarding UPFs. Initiatives aimed at promoting whole and minimally processed foods have been suggested as solutions to combat the proliferation of ultra processed items in diets. Nutritional labelling reforms and public health campaigns are necessary to inform consumers about the dangers of excessive UPF consumption.
Conclusion
As ultra processed foods continue to dominate the market, it is crucial for consumers to understand their implications on health. Being informed can empower individuals to make healthier dietary choices, which is vital in preventing lifestyle-related health issues. Future research and policy measures should focus on mitigating the consumption of these foods and promoting healthier alternatives to establish a more balanced diet for the population.
