Hepatitis B: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
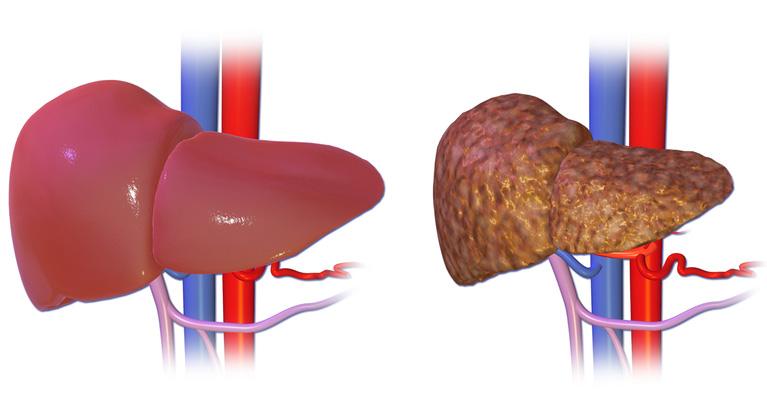
Hepatitis B is a viral infection that attacks the liver and can cause both acute and chronic diseases. It is a significant public health concern, affecting an estimated 296 million people globally, according to the World Health Organization (WHO). Understanding the importance of Hepatitis B is essential, as it can lead to severe health complications such as cirrhosis and liver cancer if left untreated, making awareness and prevention crucial for communities worldwide.
Current Statistics and Facts
The WHO’s latest reports from 2021 indicate that Hepatitis B prevalence varies widely across regions, with the highest rates in the African and Western Pacific regions. Vaccination has proven effective, with a more than 90% effectiveness rate in preventing the infection. Despite the availability of a vaccine since the 1980s, many individuals are still unvaccinated, primarily due to lack of accessibility and awareness.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Symptoms of Hepatitis B may not manifest in the early stages, leading to many cases being untreated. When they do appear, symptoms might include fatigue, abdominal pain, jaundice, and dark urine. Diagnosis typically involves blood tests to detect the presence of the virus and to measure the levels of liver enzymes, essential for assessing liver damage.
Preventive Measures
Preventing Hepatitis B infection involves vaccination, safe sex practices, and avoiding the sharing of needles or personal items that may be contaminated. The introduction of the Hepatitis B vaccination within routine immunisation schedules has shown to dramatically reduce infection rates, particularly in children.
Treatment and Management
While there is no cure for chronic Hepatitis B, treatments are available to manage symptoms and reduce the risk of liver damage. Antiviral medications can help to control the virus and lower the risk of transmission. Regular monitoring and health check-ups are critical for individuals diagnosed with the virus.
Conclusion
Hepatitis B remains a significant health issue affecting millions worldwide. While preventative measures and treatments are available, continuous efforts are required to enhance public awareness and vaccination coverage. By engaging in preventive strategies and early intervention, communities can mitigate the impact of Hepatitis B and improve overall health outcomes. The global health community must work collaboratively to ensure that everyone has access to vaccination and education regarding Hepatitis B.
