Exploring ACL Injury: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
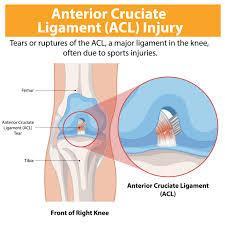
Introduction
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) injuries are among the most common knee injuries, especially in sports. With approximately 200,000 cases reported annually in the UK alone, understanding ACL injuries is crucial for athletes and coaches alike. These injuries can lead to prolonged recovery times and may even affect an athlete’s career. This article aims to highlight the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for ACL injuries.
What is an ACL Injury?
The ACL is one of the key ligaments that help stabilise the knee joint. It connects the thigh bone (femur) to the shin bone (tibia) and is vital for activities that require sudden stops, jumps, or changes in direction. An ACL injury occurs when this ligament is torn or sprained, often due to high-impact sports such as football, basketball, and skiing.
Causes of ACL Injuries
ACL injuries can result from a direct blow to the knee or from sudden changes in direction or speed. Unsurprisingly, many injuries occur during high-intensity sporting activities. However, they can also happen during daily activities, particularly in those who may have weakened ligaments due to previous injuries or lack of conditioning.
Symptoms
The symptoms of an ACL injury can vary depending on the severity of the damage but typically include:
- Sudden pain: Many individuals report hearing a pop at the moment of injury.
- Swelling: This can occur within a few hours after the injury.
- Instability: A feeling like the knee may give way when trying to walk or pivot.
Treatment Options
Treatment for an ACL injury often depends on the severity of the tear. Minor sprains may only require rest, ice, compression, and elevation (the RICE method). However, if the ligament is completely torn, more aggressive treatments such as physical therapy or surgical reconstruction may be necessary.
Rehabilitation usually involves strengthening the muscles around the knee and restoring range of motion.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing ACL injuries is possible through proper training and conditioning. Athletes are encouraged to focus on strength training, balance exercises, and flexibility programs to fortify their knees against injuries. Moreover, warming up properly before activity can significantly reduce the risk of ACL injuries.
Conclusion
ACL injuries are prevalent in the sporting world and pose a significant threat to athletes’ careers. Understanding their causes and symptoms, as well as seeking early intervention and adopting preventive measures, can help mitigate their impact. As sports continue to gain popularity, raising awareness about ACL injuries will remain essential for ensuring safer playing environments and coaching methods.
