A Comprehensive Overview of Sarcoma Cancer
Introduction
Sarcoma cancer is a rare and diverse group of cancers that arise from connective tissues such as bones, fat, nerves, and muscles. Although it constitutes less than 1% of all adult cancers, understanding sarcomas is vital due to their aggressive nature and the complex treatment options involved. With over 50 different types of sarcoma identified, raising awareness can lead to earlier detection and better patient outcomes.
Types of Sarcoma Cancer
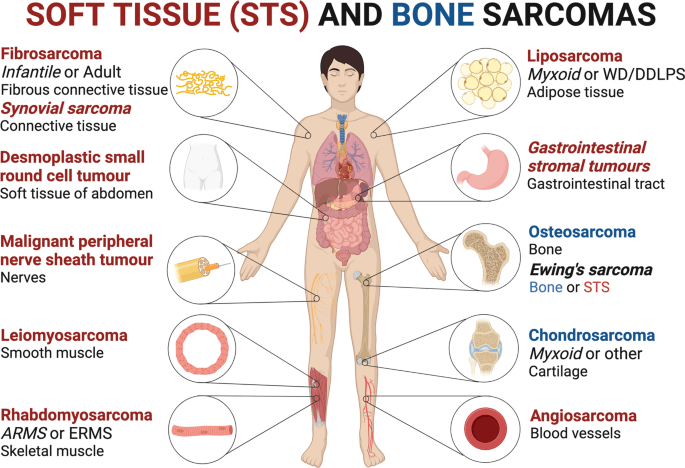
Sarcomas are mainly divided into two categories: soft tissue sarcomas and bone sarcomas. Soft tissue sarcomas may occur in muscles, fat, blood vessels, and other connective tissues, with examples including liposarcoma and leiomyosarcoma. Bone sarcomas, also known as osteosarcomas, typically affect the bones and are more prevalent in teenagers and young adults. Ewing’s sarcoma and chondrosarcoma are also notable types of bone sarcomas.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The signs and symptoms of sarcoma can vary greatly depending on the tumour’s location and size. Common symptoms include an unexplained lump or swelling, persistent pain in the affected area, and in some cases, changes in mobility. Early diagnosis can be challenging due to the rarity of the condition; however, imaging tests such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans, along with biopsies, are crucial for accurate diagnosis.
Treatment Options
Treatment for sarcoma cancer usually involves a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy, tailored to the type and stage of sarcoma. Surgery aims to remove the tumour completely, while chemotherapy and radiation can help shrink the tumour or eliminate cancer cells. Recent advancements in targeted therapies and immunotherapy are showing promise, sparking hope for more effective treatment modalities in the future.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while sarcoma cancer remains a rare and complex disease, increasing public awareness and understanding of its types, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial in improving outcomes for those affected. With ongoing research and advancements in treatment, there is optimism that the future holds better diagnostic tools and therapies, ultimately enhancing survival rates and the quality of life for patients battling this challenging cancer.
